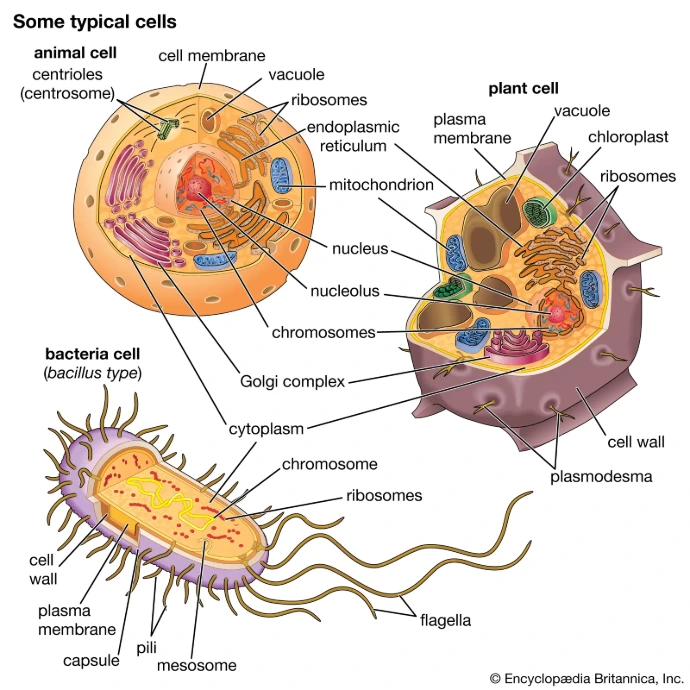
What Is a Cell?
The Fundamental Unit of Life
A cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of all living organisms. Every plant, animal, and human body is built from cells. Some organisms, like bacteria, consist of a single cell. Others, like humans, are made of trillions of cells working together.
Cells are often described as the “building blocks of life,” but they are more than blocks — they are dynamic systems that produce energy, communicate, grow, and reproduce.

Why Cells Matter in Genetics?
Inside every cell lies genetic information. This information controls:
How the cell functions
How it divides
How it responds to its environment
Understanding the cell is the first step toward understanding genes and chromosomes because genetic material lives inside cells.
What Is a Gene?
The Unit of Heredity
A gene is a specific segment of DNA that contains instructions for making a functional product, usually a protein. Genes determine inherited traits such as eye color, blood type, and susceptibility to certain diseases.
Think of a gene as a single instruction in a massive biological instruction manual.

What Does a Gene Do?
Store biological information
Guide protein production
Control cell structure and function
Influence traits and disease risk
Proteins produced by genes perform most cellular functions — from transporting oxygen to fighting infections.
What Is a Chromosome?
A chromosome is a long, organized structure made of DNA and proteins. Its role is to package DNA efficiently so it can fit inside the cell nucleus.
If DNA were stretched out, it would be about 2 meters long in each human cell. Chromosomes compact and organize this DNA.
What do you want to promote ? See more
The Blueprint of Life
Understanding the connection between cells, genes, and chromosomes is the foundation of genetics and genomics. Cells provide the environment, chromosomes organize the information, and genes carry the instructions that shape life.
From a single cell to a complex organism, life is guided by this elegant biological system structured, precise, and powerful.
Why Chromosomes Matter?
Chromosomes ensure:
Proper DNA replication
Accurate cell division
Stable inheritance of genetic information
Chromosomal abnormalities (such as extra or missing chromosomes) can lead to genetic disorders.